Contextual Multi-Armed Bandit
For the contextual multi-armed bandit (sMAB) when user information is available (context), we implemented a generalisation of Thompson sampling algorithm (Agrawal and Goyal, 2014) based on PyMC.
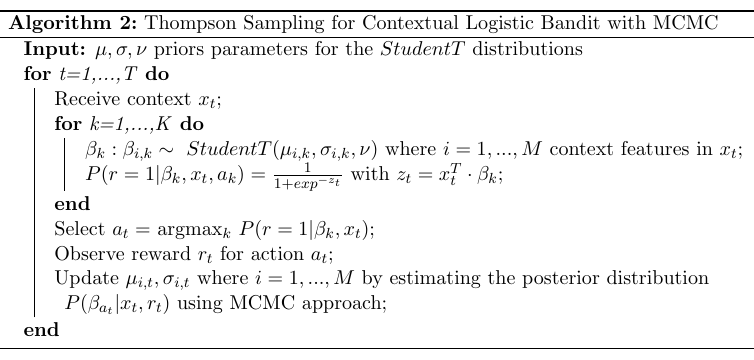
The following notebook contains an example of usage of the class Cmab, which implements the algorithm above.
[1]:
import numpy as np
from pybandits.cmab import CmabBernoulli
from pybandits.model import BayesianLogisticRegression, BnnLayerParams, BnnParams, StudentTArray
/home/runner/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/pybandits-vYJB-miV-py3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/arviz/__init__.py:39: FutureWarning:
ArviZ is undergoing a major refactor to improve flexibility and extensibility while maintaining a user-friendly interface.
Some upcoming changes may be backward incompatible.
For details and migration guidance, visit: https://python.arviz.org/en/latest/user_guide/migration_guide.html
warn(
[2]:
n_samples = 1000
n_features = 5
First, we need to define the input context matrix \(X\) of size (\(n\_samples, n\_features\)) and the mapping of possible actions \(a_i \in A\) to their associated model.
[3]:
# context
X = 2 * np.random.random_sample((n_samples, n_features)) - 1 # random float in the interval (-1, 1)
print("X: context matrix of shape (n_samples, n_features)")
print(X[:10])
X: context matrix of shape (n_samples, n_features)
[[ 0.64437861 -0.62348703 -0.04123638 -0.03637872 0.9927251 ]
[ 0.24474943 -0.51070879 0.98429166 -0.56514291 -0.14006298]
[-0.2133921 0.11991799 0.51511665 -0.81465689 -0.23574104]
[-0.09099382 -0.95144272 -0.75021782 0.21758309 0.18975486]
[ 0.65208043 0.76152656 0.06923062 0.16088639 -0.68454121]
[ 0.52959121 0.1005556 0.69140609 0.91496378 0.08910197]
[ 0.24089576 -0.00393574 -0.91410497 -0.37922814 -0.27149415]
[ 0.87870276 -0.60766078 0.35293572 -0.52789213 -0.69020885]
[ 0.16310457 -0.59904515 -0.61849702 -0.18081805 0.8173712 ]
[ 0.26060751 0.97448829 -0.18766028 0.44790734 0.40698921]]
[4]:
# define action model
bias = StudentTArray.cold_start(mu=1, sigma=2, shape=1)
weight = StudentTArray.cold_start(shape=(n_features, 1))
layer_params = BnnLayerParams(weight=weight, bias=bias)
model_params = BnnParams(bnn_layer_params=[layer_params])
update_method = "VI"
update_kwargs = {"fit": {"n": 100}, "batch_size": 128, "optimizer_type": "adam"}
actions = {
"a1": BayesianLogisticRegression(
model_params=model_params, update_method=update_method, update_kwargs=update_kwargs
),
"a2": BayesianLogisticRegression(
model_params=model_params, update_method=update_method, update_kwargs=update_kwargs
),
}
We can now init the bandit given the mapping of actions \(a_i\) to their model.
[5]:
# init contextual Multi-Armed Bandit model
cmab = CmabBernoulli(actions=actions)
The predict function below returns the action selected by the bandit at time \(t\): \(a_t = argmax_k P(r=1|\beta_k, x_t)\). The bandit selects one action per each sample of the contect matrix \(X\).
[6]:
# predict action
pred_actions, _, _ = cmab.predict(X)
print("Recommended action: {}".format(pred_actions[:10]))
Recommended action: ['a1', 'a1', 'a2', 'a1', 'a2', 'a1', 'a2', 'a2', 'a2', 'a2']
Now, we observe the rewards and the context from the environment. In this example rewards and the context are randomly simulated.
[7]:
# simulate reward from environment
simulated_rewards = np.random.randint(2, size=n_samples).tolist()
print("Simulated rewards: {}".format(simulated_rewards[:10]))
Simulated rewards: [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]
Finally, we update the model providing per each action sample: (i) its context \(x_t\) (ii) the action \(a_t\) selected by the bandit, (iii) the corresponding reward \(r_t\).
[8]:
# update model
cmab.update(context=X, actions=pred_actions, rewards=simulated_rewards)
/home/runner/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/pybandits-vYJB-miV-py3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/pytensor/link/c/cmodule.py:2968: UserWarning: PyTensor could not link to a BLAS installation. Operations that might benefit from BLAS will be severely degraded.
This usually happens when PyTensor is installed via pip. We recommend it be installed via conda/mamba/pixi instead.
Alternatively, you can use an experimental backend such as Numba or JAX that perform their own BLAS optimizations, by setting `pytensor.config.mode == 'NUMBA'` or passing `mode='NUMBA'` when compiling a PyTensor function.
For more options and details see https://pytensor.readthedocs.io/en/latest/troubleshooting.html#how-do-i-configure-test-my-blas-library
warnings.warn(
/home/runner/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/pybandits-vYJB-miV-py3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/rich/live.py:256:
UserWarning: install "ipywidgets" for Jupyter support
warnings.warn('install "ipywidgets" for Jupyter support')
/home/runner/.cache/pypoetry/virtualenvs/pybandits-vYJB-miV-py3.10/lib/python3.10/site-packages/rich/live.py:256:
UserWarning: install "ipywidgets" for Jupyter support
warnings.warn('install "ipywidgets" for Jupyter support')